Category: Good Transit
High Speed Rail-Airport Links
As somewhat of a followup to my last post on how successful high-speed rail isn’t really made for tourists, I’d like to talk about the issue of air-rail links. Those are beloved by both foreign tourists and domestic residents using them to travel abroad, and American high-speed rail planning has on occasion tried focusing on them. This has always been awkward for both environmental and ridership goals. Such links are not inherently bad, but they are often overrated in planning, especially at the level of public advocacy and shadow planning agencies, which reproduce the biases of frequent fliers.
Skipping the airports in rich Asia
The Shinkansen does not serve Narita. There were plans for it to do so but they have not been implemented. Such service would require a dedicated line, since the Shinkansen is on a different gauge from the classical JR network and the standard-gauge link between the city and the airport is owned by private railway Keisei, and Narita itself is not important enough to drive such a line, not at the urban tunneling construction costs of Japan.
But the same lack of service to airports is seen in the two most Shinkansen-like systems outside Japan, Korea and especially Taiwan. The airport is not in Taipei but in Taoyuan, and is connected to the city by an express commuter train, the Taoyuan Airport MRT, but the Taiwan High-Speed Rail system does not serve it, instead having a different Taoyuan station on the Airport MRT. Even in Korea, which uses standard gauge and runs KTX trains through on classical lines in the French style, there is no KTX service to Incheon or to Gimpo.
The issue in all three countries is that the role of the capital’s international airport is to connect passengers between the capital region and the rest of the world. Tourists visiting the capital don’t need a train to secondary cities; in South Korea, last year, 66% of tourism by spending was in Seoul, and in Taiwan, 53% of tourism by occupied hotel nights was in Taipei, New Taipei, and Taoyuan (PDF-pp. 20-21 of the 2024 annual report). Domestic residents using the airport to travel abroad are a more serious use case, but far more residents of Busan or Kaohsiung are going to their respective country’s capital than abroad, and so the airport link is not a high priority for planning.
Serving the airports in Europe if they’re on the way
Three of the four busiest airports in the EU – CDG, Schiphol, and Frankfurt (the fourth is Barajas) – have high-speed rail links. However, in all cases, it’s because they’re on the way somewhere. CDG and Frankfurt are both on valuable bypass routes around the primary city with its terminal-only train stations, so they might as well be served. Schiphol is between Rotterdam and Amsterdam, but serving it involved high-cost tunneling, on a high-speed line, HSL Zuid, that has in retrospect been more a case of imitating the TGV than responding to Dutch intercity rail needs.
In all cases, the airport link is decidedly secondary to the network, and is not a major planning goal. There are intercity trains routed into Berlin-Brandenburg, but these are intended for long-distance regional use: the extensive rail tunneling to the new airport is for various regional express trains, with a 15-minute Takt to Berlin Hauptbahnhof and four hourly Takt trains to regional destinations starting next month and only one intercity train on a two-hour Takt between Berlin and Dresden. Munich has no ICE connection, and a proposal for one never got beyond the conceptual stage because the airport-city center connection was deemed a higher priority. It’s notable that even high-cost, high-prestige air-rail links here prioritize connections to city center, and not to the national network.
The awkward environmental politics of air-rail links
High-speed rail is justified on both economic and environmental grounds. But sometimes these different justifications end up conflicting. It’s noteworthy that in the United States, a common argument for high-speed rail in California and the Northeast has been that the airports are too clogged with short-haul regional flights and if high-speed trains replaced them then the gates and runway slots would be usable by long-haul flights. This argument is made at the same time as arguments about reducing greenhouse gas emissions – but long-haul flights contribute far more emissions than short-haul ones per unit of airport capacity consumed, airport capacity not particularly caring if you’re flying 700 km or 7,000.
It’s possible to ignore the environmental effects and just focus on the economic benefits; in Europe, the broad environmental movement is neutral or even hostile to high-speed rail, viewing it as inferior to running more night trains and regional trains. But then in Europe the economic-only planning for high-speed rail does not prioritize the air links, because they are fundamentally secondary. In a country like France, the demand for high-fare rail links to CDG is to the center of Paris, not Marseille.
Reverse-Branching on Commuter Rail
Koji asked me 3.5 days ago about why my proposal for New York commuter rail through-tunnels has so much reverse-branching. I promised I’d post in some more detail, because in truth, reverse-branching is practically inevitable on every commuter rail system with multiple trunk lines, even systems that are rather metro-like like the RER or the S-Bahns here and in Hamburg.
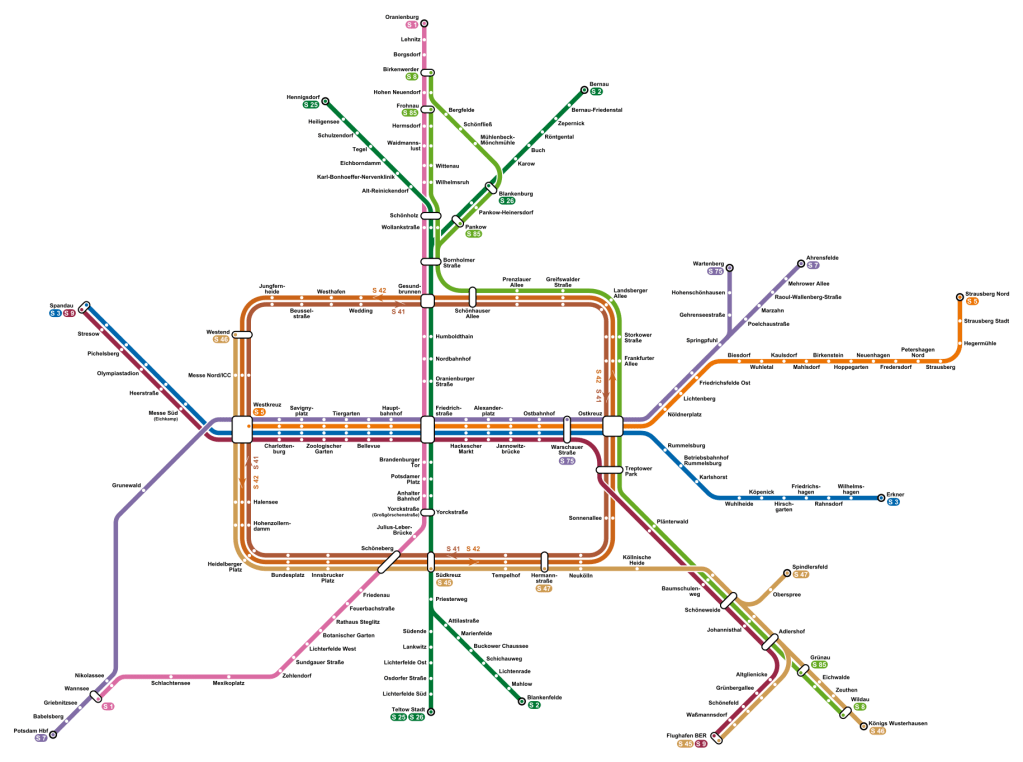
This doesn’t mean that reverse-branches, in this case the split from the Görlitzer Bahn trunk toward the Stadtbahn via S9 and the Ring in two different directions via S45/46/47 and S8/85, are good. It would be better if Berlin invested in turning this trunk into a single trunk into city center, provided it were ready to build a third through-city line (in fact, it is, but this project, S21, essentially twins the North-South Tunnel). However, given the infrastructure or small changes to it, the current situation is unavoidable.
Moreover, the current situation is not the end of the world. The reasons such reverse-branches are not good for the health of the system are as follows:
- They often end up creating more frequency outside city center than toward it.
- If there is too much interlining, then delays on one branch cascade to the others, making the system more fragile.
- If there is too much interlining, then it’s harder to write timetables that satisfy every constraint of a merge point, even before we take delays into account.
All of these issues are more pressing on a metro system than on a commuter rail system. The extent of branching on commuter rail is such that running each line as a separate system is unrealistic; tight timetabling is required no matter what, and in that case, the lines could reverse-branch if there’s no alternative without much loss of capacity. The S-Bahn here is notoriously unreliable, but that’s the case even without cascading delays on reverse-branches – the system just assumes more weekend shutdowns, less reliable systems (28,000 annual elevator outages compared with 1,800 on the similar-size U-Bahn), and worse maintenance practices.
So, on the one hand, the loss from reverse-branching is reduced. On the other hand, it’s harder to avoid reverse-branching on commuter rail. The reason is that, unlike a metro (including a suburban metro), the point of the system is to use old commuter lines and connect them to form a usable urban and suburban service. Because the system relies on old lines more, it’s less likely that they’re at the right places for good connections. In the case of Berlin, it’s that there’s an east-west imbalance that forces some east-center-east lines via S8, which was reinforced by the context of the Cold War and the Wall.
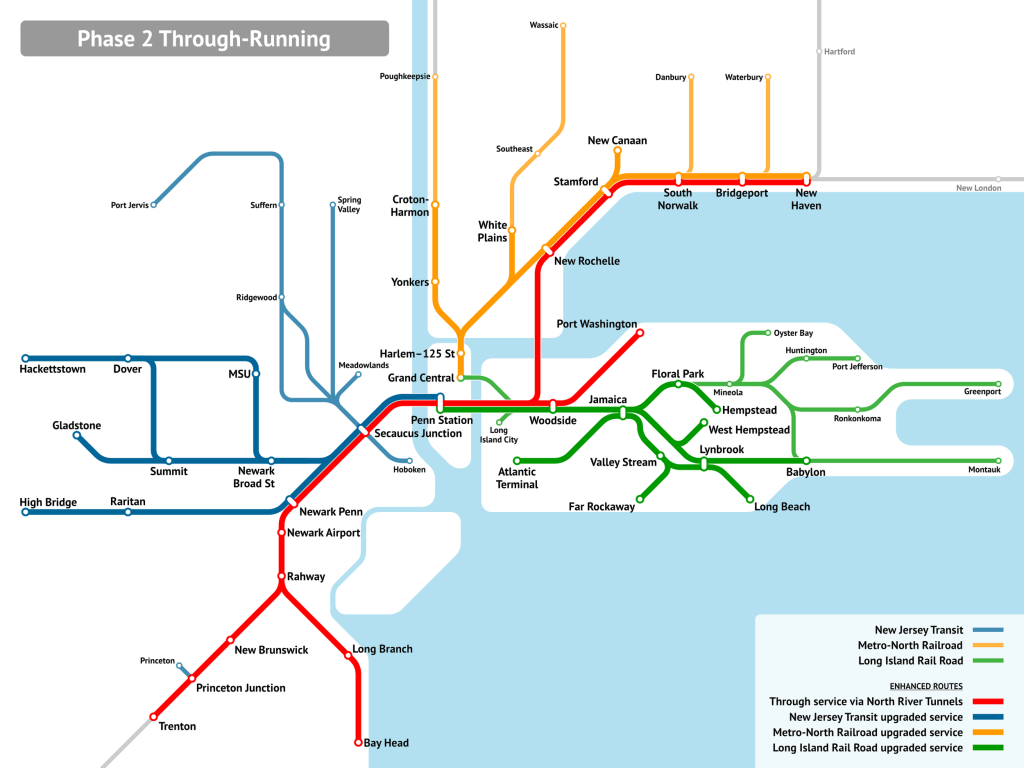
In the case of New York, consider this map:
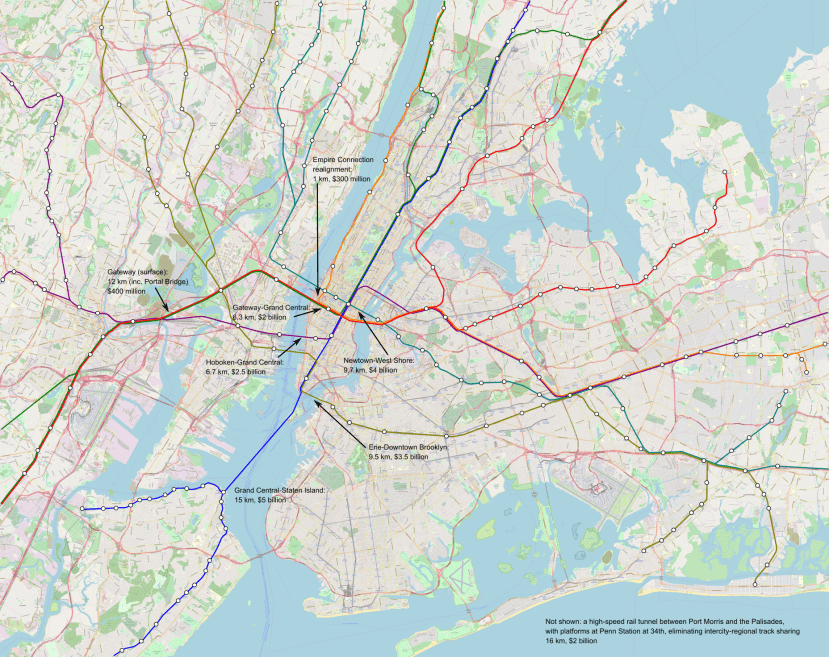
The issue is that too much traffic wants to use the Northeast Corridor lines in both New Jersey and Connecticut. Therefore, it’s not possible to segregate everything, with lines using the preexisting North River Tunnels and the new Gateway tunnels having to share tracks. It’s not optimal, but it’s what’s possible.
Timetable Padding Practices
Two weeks ago, the Wall Street Journal wrote this piece about our Northeast Corridor report. Much of it was based on a series of interviews William Boston did with me, explaining what the main needs on the corridor are. One element stands out since the MTA responded to what I was saying about schedule padding – I talk about how Amtrak and Metro-North both pad the timetables on the Northeast Corridor by about 25%, turning a technical travel time of an hour into 1:15 (best practices are 7%), and in response, the MTA said that they pad their schedules 10% and not 7%. This is an incorrect understanding of timetable padding, which speaks poorly to the competence of the schedule planners and managers at Metro-North.
The article says,
Aaron Donovan, a spokesman for the Metropolitan Transportation Authority, says the extra time built into Metro-North schedules generally averages 10%, depending on destination and length of trips, and takes into account routine track maintenance and capital work that can increase runtime. Metro-North continually reviews models, signal timing, equipment, and other elements of operation to improve travel times and reliability for customers, he says.
This is, to be clear, incorrect. Metro-North routinely recovers longer delays than 10%; delay recovery on the New Haven Line can reach well over 20 minutes out of a nominally two-hour trip, around 25% of the unpadded trip length. The reason this is incorrect isn’t that Donovan is dishonest or incompetent (he is neither of these two things), but almost certainly that the planners he spoke with genuinely believe they only pad 10%, because they, like all American railroaders, do not know how modern rail scheduling is done.
Modern rail scheduling practices in the higher-reliability parts of Europe and Japan start with the technical timetable, based on the actual speed zones and trains’ performance characteristics. This includes temporary speed restrictions. The ideal maintenance regime does not use them, instead relying on regular nighttime maintenance windows during which all tracks are out of service. However, temporary restrictions may exist if a line is taken out of service and trains are rerouted along a slower route, which is regrettably common in Germany. Modern signaling systems are capable of incorporating temporary speed restrictions – this is in fact a core requirement for American positive train control (PTC), since American maintenance practices rely on extensive temporary restrictions for work zones and one-off slowdowns. If the signal system knows the exact speed zones on each section of track, then so can the schedule planners.
The schedule contingency figure is computed relative to the best technical schedule. It is not computed relative to any assumption of additional delays due to dispatch holds or train congestion. The 7% figure used in Switzerland, Sweden, and the Netherlands takes care of the high levels of congestion on key urban segments.
The core urban networks in these countries stack favorably with Metro-North in track utilization. The Hirschengraben Tunnel in Zurich runs 18 S-Bahn trains per hour in each direction most of the day and 20 at rush hour with some extra S20 runs, and the Weinberg Tunnel runs 8 S-Bahn trains per hour and if I understand the network graphic right 7.5 additional intercities per hour. I urge people to go look at the graphic and try tracking down the lines just to see how extensively branched and reverse-branched they are; this is not a simple network, and delays would propagate. The reason the Swiss rail network is so punctual is that, unlike American rail planning, it integrates infrastructure and timetable development. This means many things, but what is relevant here is that it analyzes where delays originate and how they propagate, and focuses investments on these sections, grade-separating problematic flat junctions if possible and adding pocket tracks if not.
Were I to only take timetable padding into account relative to an already more tolerant schedule incorporating congestion and signaling limitations, I would cite much lower figures for timetable padding. Switzerland speaks of a uniform 7% pad, but in Sweden the figures include two components, a percentage (taking care of, among other things, suboptimal driver behavior) and a fixed number of minutes per 100 km, which at current intercity speeds resolve to 7% as in Switzerland. But relative to the technical trip time, the pad factors based on both observed timetable recovery and actual calculations on current speed zones are in the 20-30% range, and not 10%.
Of course, at no point do I suggest that Metro-North and Amtrak could achieve 7% right now, through just writing more aggressive timetables. To achieve Swiss, Dutch, and Swedish results, they would need Swiss, Dutch, or Swedish planning quality, which is sorely lacking at both railroads. They would need to write better timetables – not just more aggressive ones but also simpler ones: Metro-North’s 13 different stopping patterns on New Haven Line trains out of 16 main line peak trains per hour should be consolidated to 2. This is key to the plan – the only way Northern Europe makes anything work is with fairly rigid clockface timetables, so that one hour or half-hour is repeated all day, and conflicts can be localized to be at the same place every time.
Then they would need to invest based on reliability. Right now, the investment plans do not incorporate the timetable, and one generally forward-thinking planner found it odd that the NEC report included both high-level infrastructure proposals and proposed timetables to the minute. In the United States, that’s not the normal practice – high-level plans only discuss high-level issues, and scheduling is considered a low-level issue to be done only after the concrete is completed. In Northern European countries with competently-run railways and also in Germany, the integration of the timetable and infrastructure is so complete that draft network graphics indicating complete timetables of every train to the minute are included in the proposal phase, before funding is committed. In Switzerland, such a timetable is available before the associated infrastructure investments go to referendum.
Under current American planning, the priorities for Metro-North are in situ bridge replacements in Connecticut because their maintenance costs are high even by Metro-North’s already very expensive standards. But under good planning, the priority must be grade-separating Shell Interlocking (CP 216) just south of New Rochelle, currently a flat junction between trains bound for Grand Central and ones bound for Penn Station. The flat junctions to the branches in Connecticut need to be evaluated for grade-separation as well, and I believe the innermost, to the New Canaan Branch, needs to be grade-separated due to its high traffic while the ones to the two farther out branches can be kept flat.
None of this is free, but all of this is cheap by the standards of what the MTA is already spending on Penn Station Access for Metro-North. The rewards are substantial: 1:17 trip times from New Haven to Grand Central making off-peak express stops, down from 2 hours today. The big ask isn’t money – the entire point of the report is to figure out how to build high-speed rail on a tight budget. Rather, the big ask is changing the entire planning paradigm of intercity and commuter rail in the United States from reactive to proactive, from incremental to comfortable with groun-up redesigns, from stuck in the 1950s to ready for the transportation needs of the 21st century.
The Danbury Branch and Rail Modernization
I’ve been asked to talk about how rail modernization programs, like the high-speed rail plan we published at Marron this month, affect the Danbury Branch of the New Haven Line. The proposal barely talks about branch modernization beyond saying that the branches should be electrified; we didn’t have time to write precise branch timetables, which means that the timetable I’m going to post here is going to have more rounding artifacts. The good news is that modernization can be done cheaply, piggybacking on required work on the main of the New Haven Line.
Current conditions
The Danbury Branch is a 38 km single-track unelectrified line, connecting South Norwalk with Danbury making six additional intermediate stops. All stations have high platforms, but they are short, ranging between three and six cars.
Ridership is essentially unidirectional: toward Norwalk and New York in the morning, back north in the afternoon. There is little job concentration near the stations. Within 1 km of Danbury there are only 5,000 jobs per OnTheMap, rising to 10,000 if we include Danbury Hospital, which is barely outside the station’s 1 km radius (but is not easily walkable from it). Merritt 7 is in an office park, but there are only 6,000 jobs there, and nearly everyone drives. The other stations are parking lots, and Bethel is somewhat outside the town center for better parking.
The right-of-way is very curvy, much more so than the main line. Where most of the New Haven Line is built to a standard of 2° curves (radius 873 m), permitting 157 km/h with modern cant and cant deficiency, the Danbury Branch scarcely has a section straight enough with gentler curves than 3°, and much of it has such frequent 4° curves that trains cannot go faster than 100 km/h except for speedups of a few seconds at a time to recover delays.
A first pass on infrastructure and operations
It is effectively free to electrify a 38 km single-track line. The high-speed rail report estimates it at $75 million based on both European electrification costs (see report for sources) and the Southern Transcon proposal, which is $2 million/km on a busy double-track line. The junction between the branch and the main line is flat, but outbound trains can be timetabled to avoid conflict, and inbound trains have no at-grade conflict to begin with. If platform lengthening is desired, then it is a noticeable extra expense; figure $30 million for each eight-car platform, or perhaps half that on single track (but then some stops are double-track), maybe with some pro-rating for existing platforms if they can be easily reused.
The tracks should also be maintained to higher speed, which is a routine application of a track laying machine, with some weekend closures for construction followed by what should be an uninterrupted multidecade period of operations. The curves are already superelevated to a maximum of 5-6″; this is less than the 7″ maximum in US law (180 mm here), but the difference is not massive. The line has a 50 mph speed limit today for the most part, whereas it can be boosted to about 100-110 km/h depending on section, a smaller difference than taking the main line’s 70 mph and turning it into 150-160 km/h.
With a blanket speed limit of 110 km/h – in truth some sections need to dip down to 100 or even less whereas the Bethel-Danbury and Merritt 7-Wilton interstations can be done mostly at 130 – the trip time between South Norwalk and Danbury is, inclusive of 7% pad, 28.75 minutes. The Northeast Corridor report timetables have express New Haven Line commuter trains arriving South Norwalk southbound at :15.25 every 20 minutes and departing northbound at :14.75, so they’d be departing Danbury at :46.5 and arriving :43.5. Meets would occur at the :20, :30, and :40 points.
The :30 point, important as it is a meet even if service is reduced to every 30 minutes, is just south of Branchville, likely too far to use the existing meet at the station. Thus, at first pass, some additional double-tracking is needed, a total of 6 km if it covers the entire Cannondale-Branchville interstation, which would cost around $50 million at MBTA Franklin Line costs. MBTA Franklin Line costs are likely an underestimate, since the terrain on the Cannondale-Branchville interstation is hillier and some additional earthworks would be required on part of the section. A high-end estimate should be the cost of a high-speed rail line without elevated or tunneled segments, around $30 million/km or even less (cut-and-fill isn’t needed as much when the line curves with the topography), say $150 million.
The :20 point southbound is at or just south of Bethel. While this is in a built-up area, the right-of-way looks wide enough for two tracks and the topography is easier; if the station is the meet, then the cost is effectively zero, bundled into a platform lengthening project. Potentially, this could even be further bundled with moving the station slightly south to be closer to the town center. The :40 point southbound is at Merritt 7, which has room for a second track but not necessarily for a platform at it, and could instead get a second track on the opposite side of the platform if there’s enough of a rebuild to turn it into an island with additional vertical circulation; the cost of the second track itself would be a rounding error but the cost of station reconstruction would not be and would likely be in the mid-tens of millions.
How this fits into the broader system
The timetable in the report already assumes that New Haven Line service comprises 6 peak trains per hour (tph) that use the branches. The default assumption, reproduced in the service network graphic, is that New Canaan and Danbury get 3 tph each, and New Canaan gets a grade-separated junction but Danbury does not. Those trains all go to Grand Central with no through-running: only the local trains on the New Haven Line get to run through, since local trains are the highest priority for through-running. If a tunnel connecting the Gateway tunnel with Grand Central is opened, as in some long-term plans (here’s ETA’s, which isn’t very different from past blog posts’), then they can run through to it.
The establishment of this service is not going to, by itself, change the characteristic of ridership on the line. Electrification, better timetabling, and better rolling stock (in this order) can reduce the trip time from an hour today to 29 minutes, and the trip time to Grand Central from about 2:25 to 1:09, but the main effect would be to greatly improve the connectivity of existing users, who’d be driving to the parking lot stations more often, perhaps working from the office more and from home less, or taking the train to social events in the city. Some would opt to use the train to get to work at Stamford, as a secondary market. Over time, I expect that people would buy in the area to commute to work in New York (or at Stamford), but housing permit rates in Fairfield County are low and only limited TOD is likely. It would take concerted commercial TOD at the stations to produce reverse-peak ridership, likely starting with expanding the Merritt 7 office park and making it a bit less auto-oriented.
If the ridership isn’t there, then a train every 20 minutes is not warranted and only a train every 30 minutes should be provided. This reduces the double-track infrastructure requirement but only marginally, as the meets that are no longer needed are the easy ones and the one that still is is the hard one to build, south of Branchville. In effect, something like 80% of the cost provides two thirds of the capacity; this is common to rail projects, in that small cuts in an already optimized budget lead to much larger cuts in benefits, the opposite of what one hopes to achieve when optimizing cuts.
The Northeast Corridor Report is Out
Here is the link. If people have questions, please post them in comments and I’ll address; see also Bluesky thread (and Mastodon but there are no questions there yet).
Especial thanks go to everyone who helped with it – most of all Devin Wilkins for the tools, analysis, and coding work that produced the timetables, which, as the scheduling section says, are the final product as perceived by the passenger. Other than Devin, the other members of the TCP/TLU program at Marron gave invaluable feedback, and Elif has done extensive work with both typesetting and managing the still under-construction graphical narrative we’re about to do (expected delivery: mid-June). Members of ETA have looked over as well, and Madison and Khyber nitpicked the overhead electrification section in infrastructure investment until it was good. And finally, Cid was always helpful, whether with personal support, or with looking over the overview as a layperson.
Quick Note: Report on Electrification and Medium-Speed Rail Upgrades
Nolan Hicks has wrapped up nearly a year of work at Marron on a proposal called Momentum, to upgrade mainline rail in the United States with electrification, high platforms, and additional tracks where needed, short of high-speed rail. The aim is to build low- or perhaps medium-speed rail; the proposed trip times are New York-Albany in 2:05 (averaging 109 km/h) and New York-Buffalo in 5:38 to 5:46 (averaging 123 km/h). The concept is supposed to be used US-wide, but the greatest focus is on New York State, where the plan devotes a section to Network West, that is New York-Buffalo, and another to Network East, that is the LIRR, in anticipation of the upcoming state budget debate.
The costs of this plan are high. Nolan projects $33-35.6 billion for New York-Buffalo, entirely on existing track. The reasoning is that his cost estimation is based on looking at comparable American projects, and there aren’t a lot of such upgrades in the US, so he’s forced to use the few that do exist. A second track on single-track line is costed cheaply with references to various existing projects (in Michigan, Massachusetts, etc.), but third and fourth tracks on a double-track line like the Water Level Route are costed at $30 million/km, based on a proposal in the built-up area of Chicago to Michigan City.
In effect, the benefits are a good way of seeing what upgrades to best American industry practices would do. The idea, as with the costing, is to justify everything with current or past American plans, and the sections on the history of studies looking at electrification projects are indispensable. This covers both intercity and regional rail upgrades, and we’ve used some of the numbers in the drafts at ETA to argue, as Nolan does, against third rail extensions and in favor of catenary on the LIRR and Metro-North.
(Update 4-3: and now the full proposal is out, see here.)
16-Car Trains on the Northeast Corridor
The dominant length of high-speed rail platforms in China, Japan, South Korea, and Europe is 400 meters, which usually corresponds to 16-car trains. The Northeast Corridor unfortunately does not run such long trains; intercity trains on it today are usually eight cars long, and the under construction Avelia Liberty sets are 8.5 cars long. Demand even today is high enough that trains fill even with very high fares, and so providing more service through both higher frequency and longer trains should be a priority. This post goes over what needs to happen to lengthen the trains to the global norm for high-speed rail. More trains need to be bought, but also the platforms need to be lengthened at many stations, with varying levels of difficulty.
The station list to consider is as follows:
- Boston South Station
- Providence
- New London-HSR
- New Haven
- Stamford
- New York Penn Station
- Newark Penn Station
- Trenton
- Philadelphia 30th Street
- Wilmington
- Baltimore Penn Station
- BWI
- Washington Union Station
Some of these are local-only stations – the fastest express trains should not be stopping at New London or BWI, and whether any train stops at Stamford or Trenton is a matter of timetabling (the headline timetable we use includes Stamford on all trains but I am not wedded to it). In order, allowing 16-car trains at these stations involves the following changes.
Boston
South Station’s longest platforms today are those between tracks 8 and 9 and between tracks 10 and 11, both 12 cars long. To their immediate south is the interlocking, so lengthening would be difficult.
Moreover, the best platforms for Northeast Corridor trains to use at South Station are to the west. The best way to organize South Station is as four parallel stations, from west to east (in increasing track number order) the Worcester Line, the Northeast Corridor and branches, the Fairmount Line, and the Old Colony Lines, with peak traffic of respectively 8, 12 or 16, 4 or 8, and 6 trains per hour. This gives the Northeast Corridor tracks 4-7 or possibly 4-9; 4-7 means the Franklin Line has to pair with the Fairmount Line to take advantage of having more tracks, and may be required anyway since pairing the Franklin Line with the Northeast Corridor (Southwest Corridor within the city of Boston) would constrain the triple-track corridor too much, with 12 peak commuter trains and 4 peak intercity trains an hour.
The platform between tracks 6 and 7 is 11 cars long, but to its south is a gap in the tracks as the interlocking leads tracks 6 and 7 in different directions, and thus it can be lengthened to 16 cars within its footprint. The platform between tracks 4 and 5 is harder to lengthen, but this is still doable if the track that tracks 5 and 6 merge into south of the station is moved in conjunction with a project to lengthen the other platform.
Of note, the other Boston station, Back Bay, is rather constrained, with nearly the entire platforms under an overbuild, complicating any rebuild.
Providence
Providence has 12-car platforms. The southern edge is under an overbuild with rapid convergence between the tracks and cannot reasonably be extended. But the northern edge is in the open air, and lengthening is possible. The northern edge would be on rather tight curves, which is not acceptable under most standards, but in such a constrained environment, waivers are unavoidable, as is the case throughout urban Germany.
New London
This is a new station and can be built to the required length from the start.
New Haven
The current station platforms are only 10 cars long, but there is space to expand them in both directions. The platform area is in effect a railyard, a good example of the American tradition in which the train station is not where the trains are (as in Europe) but rather next to where the trains are.
A rebuild is needed anyway, for two reasons. First, it is desirable to build a bypass roughly following I-95 to straighten the route beginning immediately north of the station, even cutting off State Street in order to go straight to East Haven rather than curve to the north as on the current route. And second, the current usage of the station is that Amtrak uses tracks 1-4 (numbered west to east as in Boston) and Metro-North uses tracks 8-14, which forces Amtrak and Metro-North trains to cross each other at grade from their slow-fast-fast-slow pattern on the running line to the fast-fast-slow-slow pattern at the station. In the future, the station should be used in such a way that intercity trains either divert north to Hartford or Springfield or go immediately east on a flying junction to the high-speed bypass toward Rhode Island, without opposed-direction flat junctions; the flying junction is folded into the cost of the bypass and dominates the cost of rebuilding the platforms, as the space immediately north and south of the platforms is largely empty.
Stamford
Stamford has 12-car platforms. Going beyond that is hard, to the point that a more detailed alternatives analysis must include the option of not having intercity trains stop there at all, and instead running 12-car express commuter trains, lengthening major intermediate stops like South Norwalk (currently 10 cars long) and Bridgeport (currently 8) instead.
To keep the mainline option of stopping at Stamford, a platform rebuild is needed, in two ways. First, the station today has five tracks, a both literally and figuratively odd number, not useful for any timetable, with the middle track, numbered 1 (from north to south the numbers are 5, 3, 1, 2, 4), not served by a platform. And second, the platform between tracks 3 and 5 can at best be lengthened to 14 cars, while that between tracks 2 and 4 cannot be lengthened without moving tracks on viaducts. This means that some mechanism to rebuild the station should be considered, to create four tracks with more space between them so that 16-car platforms are viable; this should be bundled with a flying junction farther east to grade-separate the New Canaan Branch from the mainline.
A quick-and-dirty option, potentially viable here but almost nowhere else, is selective door opening, at the cost of longer dwell times. Normally selective door opening should not be used – it confuses passengers, for one. However, here it may be an option, as intercity traffic here is unlikely to be high; traffic today is 323,791 in financial 2023, the lowest of any station under consideration in this post unless one counts New London. The only reason to stop here in the first place is commuter ridership, in which case mechanisms such as restricting unreserved seats to the central 12 cars can be used.
New York
Penn Station has multiple platforms already long enough for 16- and even 17-car trains, including the one we pencil for all high-speed intercity trains in the proposal, platform 6 between tracks 11 and 12, as well as the two adjacent platforms, 5 and 7. (Note that unlike at New Haven and Boston, platform numbers at Penn increase south to north, that is right to left from the perspective of a Boston-bound traveler.)
Thank the god of railways, since platform expansion requires a multi-billion dollar project to remove the Madison Square Garden overbuild in the most optimistic case; in a more pessimistic case, it would also require removing the Moynihan Station overbuild.
Newark
Newark Penn Station’s platforms are in a grand structure about 14.5 cars long. Thankfully, they extend a bit south of it, producing about 16 cars’ worth of platform on the west (southbound) side, between tracks 3 and 4; as in New York, track numbers increase east to west. On the east side, PATH interposes between the two tracks, which have a cross-platform transfer from northbound New Jersey Transit trains to PATH. The platform structures and their extensions do have enough length to allow 16-car trains – indeed they go as long as 18 – but the southern ends are currently disused and would require some rehabilitation.
Trenton
Trenton has a 12.5 car long southbound platform and an 11.5 car long northbound platform. There is practically no room for an expansion if no tracks are moved. If tracks are moved, then some space can be created, but only enough for about 14 cars, not 16.
However, traffic is low, the second lowest among stations under consideration next to Stamford. The suite of Stamford solutions is thus most appropriate here: selective door opening with only the middle 12 cars (naturally the same as at Stamford) open to commuters, or just not stopping at this station at all. The only reason we’re even considering stopping here is timetabling-related: trains should be running every 10 minutes around New York but every 15 between Baltimore and Washington, or else significant expansion of quad-tracking on the Penn Line is required, and so a local stop should be added as a buffer, which can be Trenton or BWI, and BWI has twice the current Amtrak traffic of Trenton.
Philadelphia
30th Street Station has 14-car platforms. Selective door opening is basically impossible given the high expected traffic at this station, and instead platform expansion is required. There is an overbuild, but the tracks stay straight and only begin curving after a few tens of meters, which gives room for extension; from the north end to the overbuild to where the tracks begin curving toward one another to the south is 15.5 cars, and there is room north of the overbuild between the tracks.
Whatever reconstruction project is needed is helped by the low traffic at these platforms. SEPTA uses the upper level of the station, with tracks oriented east-west. The north-south lower level is only used by Amtrak, which could be easily reduced to three platform tracks (two Northeast Corridor, one Keystone) if need be, out of 11 today. Thus, staging construction can be done easily and intrusively, with no care taken to preserve track access during the work, as half the station platforms can be closed off at once.
Wilmington
Wilmington is frustrating, in that there is platform space for 16 cars rather easily, but it’s on inconsistent sides of the tracks. Track numbers increase south to north; track 1 has a side platform, there’s an island platform between tracks 2 and 3, and then track 3 also has a side platform on the other side, extending well to the east of the island platform. The island platform and the track 1 platform are about 12.5 cars long, and the track 3 side platform is 13.5 cars long. Thus, an extension, selective door opening, or a station rebuild is required.
The island platform can be extended about one car in each direction, so it cannot be the solution without selective door opening. Both side platforms can be extended somewhat to the west: the track 1 platform can be extended to 16 cars, but it would need to be elevated in the narrow space between the track viaduct and the station parking garage; the track 3 platform can be extended in both directions, avoiding a new elevated extension over North King Street.
If for some reason an extension of the track 1 platform is not possible, then selective door opening can be used, but not as reliably as at lower-traffic Stamford or Trenton, and overall I would not recommend this solution. A station rebuild then becomes necessary: the station has three tracks but doesn’t need more than two if SEPTA and Amtrak can be timetabled right, and then the removal of either track 1 or track 2 would create space for a longer platform.
Baltimore
Baltimore Penn has seven tracks, numbered from south to north 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, F. Their platforms are 10 to 13 cars long. Northbound trains are more or less forced to use the platform between tracks 1 and 3, since the way the route tapers to a three-, then four-track line to the east forces all eastbound trains to use mainline track 1; this platform is rather narrow at its east end but has space to the west for a 16-car extension. Westbound trains can use either the platform between tracks 4 and 5 or that between tracks 6 and 7, with tracks 4 and 6 preferred over 7 as they reach the express westbound track (track 5 stub-ends). Both platforms can be extended, with the platform between tracks 6 and 7 requiring a one-car extension to the east where a ramp down to track level for track workers exists whereas that between tracks 4 and 5 has ample unused space to its west.
BWI
The two side platforms at BWI are just under 13 cars long. However, nowhere else on the corridor is an extension easier: the station is located in an undeveloped wooded area, with space cleared on both sides of the track so that tree cutting is likely unnecessary west of the tracks and certainly unnecessary east of them.
The station itself needs a rebuild anyway, due to already existing plans to widen it from three to four tracks. This is required to enable intercity trains to overtake commuter trains anyway, unless delicate timetabling on triple track is used or another part of the Penn Line is set up as a four-track overtake. The plans are rather advanced, but platform extensions can be pursued as an add-on, without disturbing them due to the easy nature of the right-of-way.
Washington
Washington is set up as two separate stations, a high-platform terminal to the west and a low-platform through-station to the east on a lower level. Track numbers increase west to east, the western part taking 7-20 (though only 9-20 are high and wired) and the eastern part 23-30. None of the western platforms is long enough, but multiple options still exist:
- The platform between tracks 9 and 10 has room for an extension.
- The platforms between tracks 15 and 16 and between tracks 16 and 17 look like they already have extensions, if not open for passengers.
- The platforms between track 17 and track 18 and between tracks 19 and 20 are only 12 cars long, but tracks could be cannibalized in the open air to make a long enough platform, especially since the reason track numbers 21 and 22 are skipped is that there used to be tracks there and now there’s empty space.
- The platform between tracks 25 and 26 is long enough, and could be raised to have level boarding.
The existing platforms that can be extended easily are sufficient in number, but probably not in location – it’s ideal for the platforms to be close together, to simplify the interlocking as trains have to be scheduled to enter and leave the station without opposite-direction conflicts. If it’s doable even with a split between platforms separated by multiple tracks then it’s ideal, but otherwise, the extra work on tracks 17-20 may be necessary, converting a part of the station that presently has six tracks and four platforms into likely four tracks and two platforms.
Conclusion
All of this looks doable. The hardest station, Stamford, is skippable if selective door opening is unviable after all and a rebuild is too expensive. Among the other stations, light rebuilds are needed at Boston, Wilmington, and maybe Washington; New Haven needs a more serious rebuild as part of the bypass, but the station platforms are a routine extension where there is already room between the tracks. The most untouchable station, New York, already has multiple platforms of the required length at the required location within the station.
One- and Two-Dimensional Rail Networks
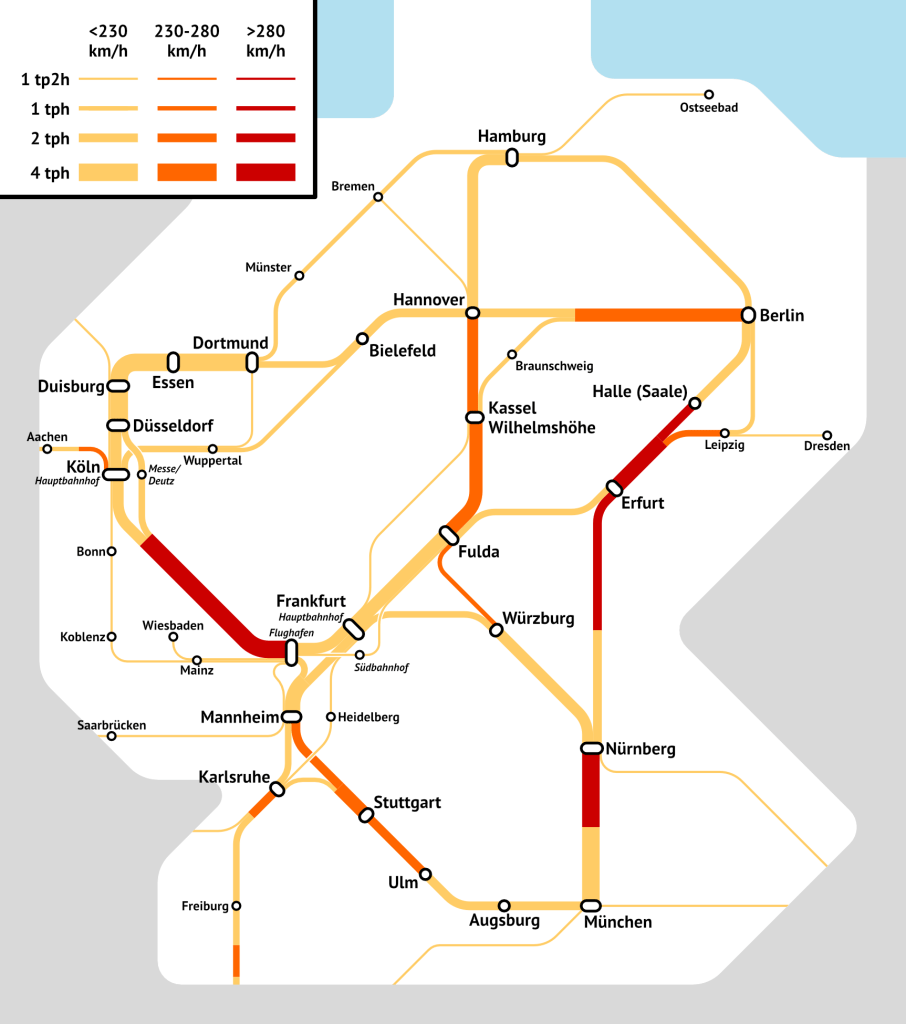
As people on social media compare the German and American rail networks, I’m going to share two graphics from the upcoming Northeast Corridor report, made by Kara Fischer. They are schematic so it’s not possible to speak of scale, but the line widths and colors are the same in both; both depict only lines branded as Amtrak or ICE, so Berlin-Dresden, where the direct trains are branded IC or EuroCity, is not shown, and neither are long-range commuter lines even if they are longer than New Haven-Springfield.
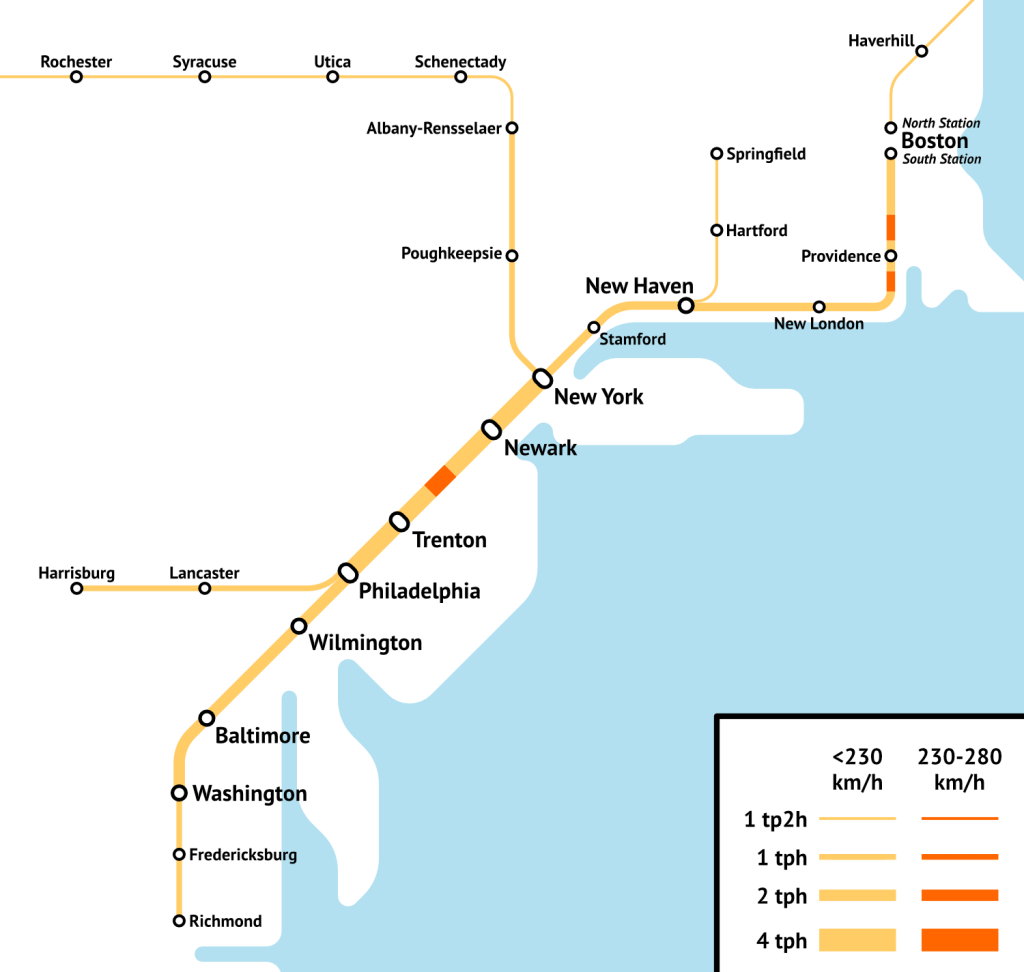
The Northeastern United States has smaller population than that of Germany but not by much (74 million including Virginia compared with 84 million), on a similar land area. Their rail networks should be, to first order, comparable. Of course they aren’t – the map above shows just how much denser the German rail network is than the American one, not to mention faster. But the map also shows something deeper about rail planning in these two places: Germany is two-dimensional, whereas the Northeastern US is one-dimensional. It’s not just that the graph of the Northeastern rail network is acyclic today, excluding once-a-day night trains. More investment in intercity rail would produce cycles in the Northeastern network, through a Boston-Albany line for one. But the cycles would be peripheral to the network, since Boston, New York, Philadelphia, and Washington are collinear on the Northeast Corridor, and the smallest of these four metro areas, Philadelphia, is larger than all those on the branches depicted above, combined.
The most important effect on network planning is that it turns the Northeast Corridor into easy mode. We would not be able to come up with a coherent timetable for Germany on the budget that our program at Marron had. In the Northeast, we did, because it’s a single line, the main difficulty being overtakes of commuter trains that run along subsections.
This, in turn, has two different implications, one for each place.
The one-dimensionality of the Northeast
In the Northeast, the focus has to be on compatibility between intercity and commuter trains. Total segregation of tracks requires infrastructure projects that shouldn’t make the top 50 priorities in the Northeast, especially at the throats of Penn Station, South Station, and Washington Union Station. Total segregation of tracks not counting those throats requires projects that are probably in the top 50 but not top 20. Instead, it’s obligatory to plan everything as a single system, with all of the following features:
- Timed overtakes, with infrastructure planning integrated into timetable design so that the places with overtakes, and only the places with overtakes, get extra tracks as necessary.
- Simpler commuter rail timetabling, so that the overtakes can be made consistent, and so that trains can substitute for each other as much as possible in case of train delays or cancellation.
- Higher-performance commuter rail rolling stock, to reduce the speed difference between commuter and intercity trains; the trains in question are completely routine in German regional service, where they cost about as much as unpowered coaches do in the United States, but they are alien to the American planning world, which does not attend InnoTrans, does not know how to write an RFP that European vendors will respect, and does not know what the capabilities of the technology are.
- Branch pruning on commuter rail, which comes at a cost for some potential through-running pairs – trains from New Jersey, if they run through to points east of Penn Station, should be going to the New Haven Line and Port Washington Branch, and probably not to Jamaica; Newark-Jamaica service is desirable, but it would force dependency between the LIRR and intercity trains, which may lead to too many delays.
In effect, even an intercity rail investment plan would be mostly commuter rail by spending. The projects mentioned in this post are, by spending, almost half commuter rail, but they come on top of projects that are already funded that are commuter rail-centric, of which the biggest is the Hudson Tunnel Project of the Gateway Program. This is unavoidable, given the amount of right-of-way sharing between intercity trains and the busiest commuter rail lines in the United States. The same one-dimensionality that makes intercity rail planning easier also means that commuter rail must use the same non-redundant infrastructure that intercity rail does, especially around Penn Station.
The two-dimensionality of Germany
A two-dimensional network cannot hope to put all of the major cities on one line, by definition. Germany’s largest metro areas are not at all collinear. In theory, the Rhine-Ruhr, Frankfurt, Stuttgart, and Munich are collinear. In practice, not only does this still exclude Berlin and Hamburg, which is not at all like how Northeastern US collinearity works, but also the Rhine-Ruhr is a two-dimensional polycentric region, and Frankfurt is a terminal station oriented in such a way that a Stuttgart 21-style through-running project would allow for through-service from Stuttgart or from Cologne to points east but not from Stuttgart to Cologne. There’s also a tail of regions in the 1-1.5 million population range – Leipzig, Dresden, Nuremberg, Hanover, Karlsruhe – that are collectively larger than the largest single-core region (Berlin), even if they’re still smaller collectively than the eight-core Rhine-Ruhr region. The highest-demand link, Frankfurt-Mannheim, is a bottleneck between many city pairs, and is not at all dominant over other links in frequency or demand.
This makes for a network that is, by necessity, atypically complex. Train delays between Frankfurt and Mannheim can cascade as far as Berlin and Hamburg. There are timed connections, timed overtakes of slower regional trains on shared links (more or less everything in yellow on the map), and bypasses around terminal stations including Frankfurt and Leipzig as well as around Cologne, which is a through-station oriented east-west permitting through-service from Belgium and Aachen to the rest of Germany but not between Frankfurt and Dusseldorf.
Not for nothing, Deutsche Bahn has not really been able to make all of this work. The timetable padding is around 25%, compared with 10-13% on the TGV, and even so, delays are common and the padding is evidently not enough to recover from them.
The solution has to be reducing the extent of track sharing. The yellow lines on the map should not be yellow; they should be red, with dedicated passenger-only service, turning Germany into a smaller version of China. The current paradigm pretends Germany can be a larger version of Switzerland instead. But Switzerland builds tunnels galore to go around strategic bottlenecks, and even then makes severe compromises on train speeds – the average speeds between Zurich, Basel, and Bern are around 100 km/h, which works for a country the size of Switzerland but not for one the size of Germany, in which even the current 130-150 km/h average speeds are enough to get rail advocates to never take any other mode but not enough to get other people to switch.
In effect, the speed vs. reliability tradeoff that German rail advocates think in terms of is fictional. The two-dimensionality of Germany means that the only way to run reliably is not to have high frequency of both fast and slow trains on the same tracks between Berlin and Halle, between Munich and Ingolstadt, between Hanover and Hamburg, etc. Eliminating the regional trains is a nonstarter, so this means the intercity trains need to go on passenger-dedicated tracks.
In contrast, careful timetabling of intercity and regional trains on the same line has limited value in Germany. The regional trains in question have low ridership – the core of German commuter rail is S-Bahn systems that run in dedicated city center tunnels and have limited track sharing with the rest of the network, much less with the ICEs. If there’s high regional traffic on a particular link, it comes from combining hourly trains on many origin-destination pairs, in which case trains cannot possibly substitute for one another during traffic disturbances, and timetabling with low padding is unlikely to work.
Like Takt-based planning for Americans, building a separate intercity rail network for Germans comes off as weird and foreign. France and Southern Europe do it, and Germans look down on France and Southern Europe almost to the same extent that Americans look down on Europe. But it’s the only path forward. If anything, this combination of speed with reliability means that completing an all-high-speed connection on a major trunk line, like Berlin-Munich or Cologne-Munich, would permit cutting the timetable padding to more reasonable levels, which would save time on top of what is saved by the higher top speed. Germany could have TGV average speeds as part of this system, if it realized that these average speeds are both necessary and useful for passengers.
Mass Transit on Orbital Boulevards
Herbert in comments has been asking me about urban rail on ring roads; Nuremberg has such a road with an active debate about what to do with it. Ring roads are attractive targets for urban rail, since they tend to be wide commercial throughfares. The one in Nuremberg is especially attractive for a tramway, or possibly a medium-capacity metro if one can be built cheaply; this is an artifact of its circumference (18 km) and the city’s size, reminiscent of the Boulevards of the Marshals hosting Paris Tramway Line 3, and the Cologne Gürtel, most of whose length has a tramway as well. Significantly closer-in ring roads, often delineating the medieval or Early Modern walls, are too small for this.
The history of such rings tends to be that they were built based on the extent of the industrial city. Cologne’s was built in the 19th century to connect growing bedroom communities to one another, where they previously only extended along the radial boulevards connecting them to the historic center. The Boulevards of the Marshals delineated the inner end of the Thiers wall from the 1840s; the Périphérique motorway is where the outer end had been. The upshot is that the construction standards are rather modern – for one, the roads are wide. Another upshot is that those roads are often destinations in and of themselves, so that radial rail lines have stops at them; the Métro has stops at every intersection with the Boulevards of the Marshals, generally named after the nearby gate (for example, I lived near Porte de Vincennes, due east along Métro Line 1).
This contrasts with older rings, including one visible on the screenshot above. Those older rings come from premodern city walls, and may not always have enough width to make it easy to build two tram lanes in the center or to do cheap cut-and-cover without disturbing the residences and businesses too much. Even when they do, they’re so close to the center the time savings from a ring at that radius are moderate. Jarrett Walker has long pointed out that people don’t travel in circles, giving the example of the Vienna Ring Road, which has two U-Bahn lines on different sections of it but no continuous ring, as a 5.3 km circle is too small to have viable long relatively linear sections. In Paris, old boulevards closer in than the ring forming Métro Lines 2 and 6 generally have Métro stops but it’s inconsistent, and there’s no coherent circular route to be built.
The modal question – tram or metro – is complicated by special elements of orbital boulevards, which sometimes cancel out, and can work differently in different cities.
In favor of light rail, there’s the issue of speed. Normally, the advantage of subways over tramways is that they’re faster. However, on a circumferential route, the importance of speed is reduced, since people are likely to only travel a relatively short arc, connecting between different radials or from a radial to an off-radial destination. What are more important than speed on such a route are easy transfers and high frequency. Easy transfers could go either way: if the radial routes are underground then it may be possible to construct underground interchanges with short walking, but it isn’t guaranteed, and if there are any difficulties, it’s better to keep it on the surface to shorten the walk time. This has in general been an argument used by pro-tram, anti-subway advocates in Germany, but on routes that rely on multiple transfers, potentially three-legged trips, it is a stronger argument than on a radial line from a suburban housing project to city center.
Frequency is especially delicate. It can be high regardless of mode. Driverless metros can reach 90-second headways or even less, but those are achieved on very busy lines, which need that frequency for throughput more than anything, like Lines 1 and 14 in Paris with their 85-second peak headways. In practice, an orbital tram, especially one in a smaller city than Paris, needs to be prioritizing frequency in order to shorten the trip, not to provide very high throughput, which means that the vehicles could be made smaller than full-size metros, to support frequency in the 3-6 minute range. This could be done at-grade with light rail, or underground with very small-profile metros akin to those used in small Italian cities like Brescia, or even some larger ones like Turin.
In favor of metro, there is the cost issue. The same factors that make speed less important and frequency more important also make it easier to build a metro. If the road is wide enough, which I think the one in Nuremberg is, then cut-and-cover is more feasible, reducing costs. The low required capacity permits intermediate-capacity metros (again, as in Brescia or some smaller French cities), with stations of perhaps 40-50 meters, reducing their construction costs. Nuremberg in particular has had some very low U-Bahn construction costs, so its ability to build an orbital U-Bahn should not be discounted. That said, even at Nuremberg costs – around $100 million/km in 2023 PPPs for U3 extensions – the extra speed provided by such a line, say half an hour to do a full orbit compared with a little less than an hour on a tram, may not be worth it necessarily, whereas such a speedup on a line that passengers may ride for 10 km unlinked would be extremely beneficial.
Quick Note: Flushing’s Growth and Through-Running
One of the dirty secrets of my (and ETA’s) New York commuter rail through-running proposal is that it barely connects Long Island to New Jersey. The later lines with the longer greenfield tunnels do, but the base proposal only through-runs the Port Washington Branch to New Jersey, and with some work it can also through-run some branches to the Hudson Line via Penn Station.
Credit: Kara Fischer, ETA; Flushing is not depicted on the map and is on the Port Washington Branch
It’s long been a criticism of the plan in comments and on social media that it doesn’t do anything to connect Newark with Jamaica. I’d like to address this briefly, since changes in work geography over the last decade have made the Port Washington connection more valuable relative to the Jamaica connection.
Job counts
For the main secondary centers that are or could be on this system, here are the job counts within 1 km of the station, in the business cycle peak years of 2007 and 2019:
| Station | 2007 jobs | 2019 jobs |
| Newark Penn Station | 57,944 | 44,171 |
| Sunnyside – Queens Boulevard | 40,092 | 63,096 |
| Flushing | 17,026 | 42,961 |
| Jamaica | 11,880 | 20,130 |
| Stamford | 25,189 | 25,141 |
Source: OnTheMap
Jamaica and Flushing both grew rapidly in the 2007-19 business cycle, but Flushing both started bigger and grew faster, to the point of approaching the job count near Newark Penn Station.
Long Island City has seen booming development, as the only near-center neighborhood in New York with significant construction rates; the number of residents has grown even faster, from 4,502 to 12,183 employed residents over the same period, but with a jobs-to-employed-residents ratio higher than 5, it is a business district first. Plans for an infill station at Queens Boulevard are on the MTA’s wishlist in the 20 Year Needs Assessment, at typically extreme MTA costs; this is separate from Sunnyside Junction, somewhat to the east, which has less development but could be a cross-platform transfer with East Side Access-bound trains.
Non-work trips
Flushing is a booming ethnic center for Chinese-New Yorkers. Jobs there serve the community wherever its members live, and so do non-work destinations, including cultural centers and well-regarded Chinese restaurants. This generates not only work trips, but also consumption trips. Without fast transit to Flushing, it’s a special occasion to go there for food, especially if one does not live on the subway; with fast transit, Flushing restaurants are capable of outcompeting more local alternatives for people arriving from inner New Jersey, and people from suburbs farther out may choose to take a more frequent LIRR than to drive.
Jamaica is not a regional center of much. There is one big trip generator there, other than the growing job center: JFK, via the AirTrain. Airport connections are valuable, but also overrated. The unlinked (likely total) ridership on the AirTrain in the first three months of 2024 was 1.924 million, or 21,143/day (not weekday), slightly higher than in 2019. This is not a high modal split, but airport arrivals are disproportionately going to Manhattan already, and the frequency between Penn Station and Jamaica is high enough that through-running and other modernization elements would only mildly increase this figure.
I can’t quite compare the two figures, since leisure trips, especially routine ones like going out to restaurants, are hard to measure. But Jamaica’s airport trips coming from better commuter rail are just not going to be significant in volume by the standards of the work trips of Long Island City or Flushing.
Through-running schemas
The reason I’ve advocated for through-running from New Jersey to the Port Washington Branch and no other LIRR line is operational. There is only enough capacity for at most 12 trains per hour, because the trains have to share tracks with Penn Station Access local trains to Stamford and with intercity trains. Connecting to an LIRR branch serving Jamaica would create complex branching, with the same line in Queens reverse-branching to different destinations, reducing reliability. It was hard enough to timetable the reverse-branched New Haven Line in our Northeast Corridor project. The Port Washington Branch, running completely separately from the rest of the system, sharing tracks only on the approach to and within Penn Station, is an ideal candidate.
It is a happy coincidence that the through-running schema for the LIRR that is easiest to implement also happens to serve the larger Queens business center between the two traditional ones. It would also be a great opportunity to build infill in Long Island City, which has emerged in the last few decades to be a much larger center. Another happy coincidence is that, while New Haven Line timetabling has been difficult, there is room in the schedule for two infill stations in Queens without upsetting the delicate track sharing between Penn Station Access local commuter trains and intercity trains within the East River Tunnels to Penn Station. Anything involving mainline rail through legacy cities is necessarily going to have to rely on tricks, waivers, and happy coincidences like this to cobble together a good system out of a region that had no reason to be built in 1900-30 around the commuter rail technology of the 1970s-2020s.